Portal:Yemen
Yemen Portal


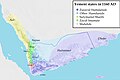
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to the north, Oman to the northeast, the Red Sea to the west, and the Indian Ocean to the south, sharing maritime borders with Eritrea, Djibouti and Somalia across the Horn of Africa. Covering roughly 528,000 square kilometres (203,861 square miles), with a coastline of approximately 2,000 kilometres (1,200 miles), Yemen is the second largest country on the Arabian Peninsula. Sanaa is its constitutional capital and largest city. Yemen's estimated population is 34.7 million, mostly Arab Muslims. It is a member of the Arab League, the United Nations, the Non-Aligned Movement and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation.
Owing to its geographic location, Yemen has been at the crossroads of many civilisations for over 7,000 years. In 1200 BCE, the Sabaeans formed a thriving commercial kingdom that included parts of modern Ethiopia and Eritrea. In 275 CE, it was succeeded by the Himyarite Kingdom, which spanned much of Yemen's present-day territory and was heavily influenced by Judaism. Christianity arrived in the fourth century, followed by the rapid spread of Islam in the seventh century. Yemenite troops playing a crucial role in early Islamic conquests. Various dynasties emerged between the 9th and 16th centuries. During the 19th century, the country was divided between the Ottoman and British empires. After World War I, the Kingdom of Yemen was established, which in 1962 became the Yemen Arab Republic (North Yemen) following a coup. In 1967, the British Aden Protectorate became the independent People's Democratic Republic of Yemen (South Yemen), the first and only officially socialist state in the Arab world. In 1990, the two Yemeni states united to form the modern Republic of Yemen, with Ali Abdullah Saleh serving as the first president until his resignation in 2012 in the wake of the Arab Spring.
Since 2011, Yemen has been enduring a political crisis, marked by street protests against poverty, unemployment, corruption, and President Saleh's plan to amend Yemen's constitution and eliminate the presidential term limit. By 2015, the country became engulfed by an ongoing civil war with multiple entities vying for governance, including the Presidential Leadership Council of the internationally recognized government, and the Houthi movement's Supreme Political Council. This conflict, which has escalated to involve various foreign powers, has led to a severe humanitarian crisis. (Full article...)
Selected article -
The North Yemen civil war (Arabic: ثورة 26 سبتمبر, romanized: Thawra 26 Sabtambar, lit. '26 September Revolution') was a civil war fought in North Yemen from 1962 to 1970 between partisans of the Mutawakkilite Kingdom and supporters of the Yemen Arab Republic. The war began with a coup d'état carried out in 1962 by revolutionary republicans led by the army under the command of Abdullah as-Sallal. He dethroned the newly crowned King and Imam Muhammad al-Badr and declared Yemen a republic under his presidency. His government abolished slavery in Yemen. The Imam escaped to the Saudi Arabian border where he rallied popular support from northern Zaydi tribes to retake power, and the conflict escalated rapidly to a full-scale civil war.
On the royalist side, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, and Israel supplied military aid, and Britain gave covert support. The republicans were supported by Egypt (then formally known as the United Arab Republic) and were supplied warplanes from the Soviet Union. (Full article...)List of selected articles
|
|---|
Selected biography -
List of selected biographies
|
|---|
General images -
Selected city -

Aden (Arabic: عَدَنْ, romanized: ʿAdan, Old South Arabian: 𐩲𐩵𐩬) is a port city located in Yemen in the southern part of the Arabian peninsula, positioned near the eastern approach to the Red Sea. It is situated approximately 170 km (110 mi) east of the Bab-el-Mandeb strait and north of the Gulf of Aden. With its strategic location on the coastline, Aden serves as a gateway between the Red Sea and the Arabian Sea, making it a crucial maritime hub connecting Africa, Asia, and the Middle East. As of 2023, Aden City has a population of approximately 1,080,000 residents, making it one of the largest cities in Yemen.
The city, with its rich trade history, embraces a vibrant blend of Arabic, Indian, and African influences. Positioned near the Bab Al-Mandab Strait, a vital maritime route, it serves as a crucial seaport. The city boasts key infrastructure like Aden International Airport and notable healthcare institutions including Aljoumhouria Teaching Hospital (Queen Elizabeth II), Aden General Hospital, and Friendship Teaching Hospital. Aden is divided into eight districts: Tawahi, Mualla, Crater, Khur Maksar, Al Mansura, Dar Sad, Sheikh Othman, and Al Buraiqa. These form today's Aden Governorate. During British Colonialism, Aden referred to the area along the north coast of the Gulf of Aden, encompassing Tawahi, Mualla, Crater, and much of Khur Maksar District. The western harbor peninsula, known as Little Aden, now falls within the Al Buraiqa District. (Full article...)Selected picture -
Selected cuisines, dishes and foods -
List of articles
|
|---|
Related portals
Religions in Yemen
Arab states
Related portals
Categories
Topics
Related portals
Religions in Yemen
Arab states
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus